Overview
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) has grown to address diversified and advanced tasks. Commencing from research institutes with smaller models, development and adoption of AI has now moved to applications across verticals and evolved to more complicated models. NVIDIA’s GPU Technology Conference (GTC) is one of the most critical events for advanced AI development and applications.

AI computing power at the data center and four key AI applications
The development of processors to boost computing performance faces a bottleneck to match the pace of Moore’s law. GPUs can fuel the momentum to accelerate deep learning based on the capability of parallel computing.
This year’s conference focused on the cloud-server platform HGX-2. NVIDIA provides the “building block” as a reference standard to accelerate the adoption of the architecture. The latest architecture accommodates both HPC and AI workloads for versatile needs in data centers.
“This is the supercomputer that goes to the data center, and this is the future of computing,” said NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang.
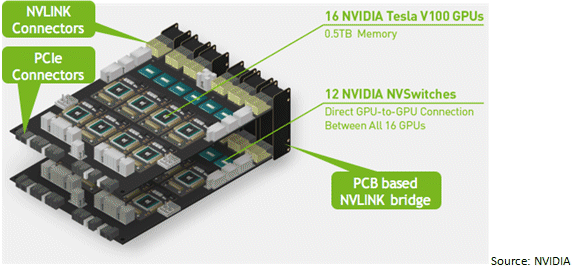
Huang emphasized the prospect of computing power for the data center, displaying the DGX-2 at the analyst roundtable. The DGX-2 system is based on HGX-2 architecture with 16 of the latest 32G V100 GPUs. The new system reaches 2 PFLOPS. The company’s breakthrough interconnection technique, NVSwitch, tremendously expands the GPU-to-GPU connection.
The conference stressed four vertical AI applications besides supercomputing and AI. The applications include autonomous driving simulation and remote intervention, RTX ray tracing technology for entertainment, CLARA platform for medical imaging, and the Metropolis platform for cities.
Outlook
Highlights of this year’s first overseas GTC 2018 include:
1. Multi-precision to handle both AI and HPC workloads
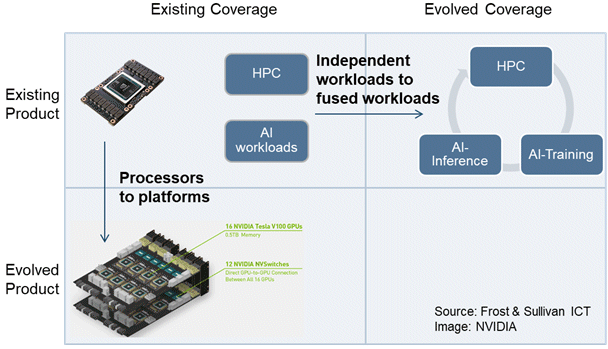
Previously, the coverage of computing workloads was independent of HPC and AI workloads. NVIDIA’s HGX-2 intends to cater to more data center markets, which is a departure from targeting only first-tier hyperscale data centers.
The new architecture allows the computing power to be available to HPC, training, and inference workloads in a single platform to accommodate the versatile needs of FP64 to Int8. The accessibility of multi-precision not only lowers the required memory and reduces the execution time for particular workloads but also enables data centers to adopt multifarious tasks and expand to broader markets.
2. More than a Processor Maker
NVIDIA’s products move it to the platform level. The announcement of HGX-2 demonstrates the company’s advancements around the world and echoes the rationale for selecting the first overseas conference location this year. “In the last 10 years, Taiwan produced 100 million servers for data centers, representing 90% of all of servers produced in the world,” Huang mentioned in his keynote.
The first DGX-2 based on the HGX-2 architecture will be available in the third quarter of this year with a price tag of $399,000—the highest-priced standard single server. NVIDIA announced that it would partner with leading server manufacturers such as Quanta, Wiwynn, Foxconn, Inventec, QCT, Lenovo, and Super Micro to create servers based on the HGX-2 system.
The cost of server platforms based on the HGX-2 reference will be higher than the DGX-2, which raised concerns about users’ willingness to invest in the high-end platform. However, HGX-2 is a way to demonstrate NVIDIA’s capability to develop a complicated system and provide a product line with a greater margin in the future.
3. AI application with safety measure for autonomous machines
Safety is a critical topic in the adoption of AI. Particularly, the safety and responsibility of autonomous driving draw people’s attention, especially after a fatal car accident in March. In addition to the pre-road test through NVIDIA’s DRIVE simulation platform, NVIDIA allows human intervention to control the car on-road to strengthen on-site safety through the VR holodeck environment.
Allowing human interventions to control autonomous vehicles and even broader types of machines increases the level of safety when the machine cannot be operated by the core system automatically.
Last word
This year’s GTC did not delve into the AI for edge computing, but the company announced its Jetson Xavier for intelligent machines at Computex Taipei five days after the conference. NVIDIA shows ambition with product development expansion and workload coverage of a wider spectrum of the market.
Authored by:
Amy Lin, Industry Analyst, Cognitive Industry (AI and IoT), ICT Research, Frost & Sullivan
Mark Koh, Associate Director, Cognitive Industry (IoT and AI), ICT Research, Frost & Sullivan



