A lot has been written about the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) or the 4th industrial revolution, and how it is in changing the face of automotive, manufacturing, aerospace, and agriculture industries. This article examines the different ways in which Industry 4.0 can be applied to pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The pharma industry faces several challenges related to quality, productivity and wastage and IIoT can help the industry tackle these challenges. Pharma 4.0 is the term used to describe Industry 4.0 in a pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape.
Today, pharma manufacturers the world over are required to remain competitive in an ever-growing market of increasing complexity. The pharma industry is one of the most heavily regulated industries, and there is always a constant need for continuous product monitoring as laid down by mandates from regulatory authorities. Traditionally, an annual quality review was sufficient; however, this is no longer the case, as there is a growing expectation from manufacturers to carry out systematic reviews more frequently than before. Advancements such as IIoT allow continuous, real-time monitoring of such processes. This helps manufacturing companies make sure that there aren’t any deviations from prescribed parameters. Any untoward incident can be predicted and rectified, thereby avoiding any down time or monetary loss which may damage the reputation of a pharma manufacturer. This is further accelerated by mounting pressures on R&D departments to not just develop products quicker but also deliver more individualized therapies.
Pharma 4.0 enables connectivity of machines, manpower, and computers at various levels. Self-aware, connected components of a smart pharma factory can: report on their own condition, suggest date of expiry and accurately predict a failure or breakdown. As a result, there is huge savings in terms of averted down time. But, in order to fully reap the benefits of sensors and the data that is generated through them, all of this data needs to be processed using advanced analytical tools and algorithms. Aspects such as predictive analytics and cognitive Intelligence are set to play a significant role in this area.
Analytics plays an important role in extracting data from sources that have been otherwise disconnected from one another; in addition, it looks for patterns, relationships and trends that were previously undetectable. Digitization of assets, data, and processes in the manufacturing value chain can thus help tap greater benefits for the pharma industry, thereby enabling the transition of the industry to a more result-oriented ecosystem. The following is an illustration of some of the key application of IIoT in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
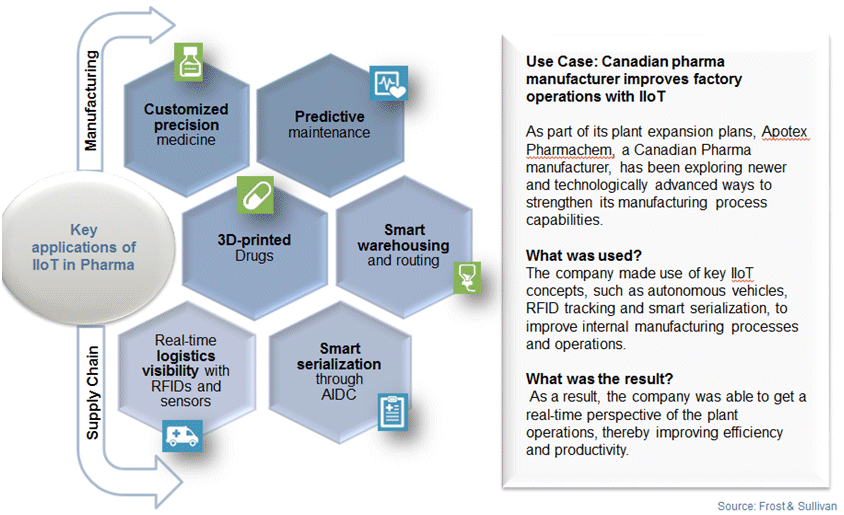
Despite all the numerous ways in which IIoT can be beneficial to pharma manufacturing, certain challenges do exist.
- The cost of upgrading all legacy equipment to more digitized equipment is a barrier, but this cost can be quickly offset by tangible results: higher productivity and a reduction in down time and waste.
- Finding adequately skilled manpower with advanced skill sets (e.g., thorough understanding of analytics) is also proving difficult, as academia struggle to anticipate strategic skills requisite for the industry in the coming years. Despite the lack of clarity, it is certainly clear already that advanced analytical skills will continue to be in demand in the years to come.
- Security is a prime concern, as Pharma 4.0 would mean connecting several hundreds of thousands of devices such as sensors, machines and networks. Each connection in turn could be a potential point of weakness from the point of view of system security. Therefore, to completely reap the benefits of Pharma 4.0, manufacturing companies will need to mitigate these security risks by becoming more open to investing in skilled security personnel.
The Pharma 4.0 topic is still far from being completely understood; progress so far has been baby steps towards a not-so-clear destination. However, the following are some guidelines for companies looking to adopt the benefits of Pharma 4.0 within their factories.
- Several crucial factors such as automation, quality, workforce, efficiency, integration, and collaboration will play a fundamental role in shaping pharma smart factories of the future. Companies should be able to address all these factors to ensure that their Pharma 4.0 programs are sustainable in the long run.
- Companies should proactively start working with other stakeholders in the supply to create a system where data, raw materials, and products, can move faster and more efficiently. Machine and equipment vendors must play an active role in streamlining these operations
- Companies must be willing to invest in R&D and encourage technological innovation new equipment, software and services) that can seamlessly integrate with each another and function as one smart entity. Data in any form has value. Advanced analytics can be made to perform analysis on already existing data sets to provide useful insights.
- Though Pharma 4.0 may appear to be talking all about smart machines, integration, smart methodologies and efficient processes, it all boils down to the most powerful asset any company—its workforce. The human element is a key success driver for any 4.0 implementation. Suitable efforts should therefore be taken to nurture talent and safeguard the interests of workforce.
One must also understand that the objective of Industry 4.0 is not to do away with people and replace them with faster, more efficient machines. It is instead, to encourage humans to co-exist and work with machines on value-added activities where the creativity and problem -solving capabilities of the human brain can be made use of to its fullest extent.
Despite pharma manufacturing being a risk-averse industry, it has the support of regulators as it takes baby steps toward Pharma 4.0. The barriers will come down with time, and Pharma 4.0 will become the new standard within the pharma industry.



