Introduction
Globally oil and gas industry continues to grow, where gas demand is expected to grow faster at an average of 1.6% year on year till 2024. The oil and gas industry is a front runner on the migration from industry 3.0 to industry 4.0, and rightfully so. Given the highly diversified and complex operations, processes, infrastructure, and human workforce, the oil and gas industry is well poised to be a leader in industry 4.0 transformation. As far as the demand for oil is concerned, the bulk of it will continue to come from the transportation industry. The global market trends indicate the continued growth in off shore platforms in deep sea, and further from the shores. Oil and gas platforms’ remoteness and isolation, harsh sea conditions, strong and unpredictable winds, water, extreme temperatures, and distance from the shore are some of the many challenges strengthening the need for a robust communications system. Routine operations alone require transmission of an insuperable volume of data and reports on logistics, supply, production etc.
Many of the communications from oil and gas platforms to site and vessels depend on satellite links, which are not only expensive, but also complex to implement and manage at such a remote location. Each surrounding vessel requires a dedicated link, and another link establishing a connection between the vessel and the offshore platform. According to various estimates, the cost per link could be in excess of $200,000 annually. Furthermore, it only provides voice communications within a restricted range of a few miles, and that too not in real time.
With the development of telecommunication technologies, the options for offshore communications have evolved too. These technologies are now making the communication simple, easy, cost efficient, and most importantly highly reliable and fast. 5G is one of the leading technologies that could add significant value to oil and gas companies by providing ultra-high speed and low latency communication between drilling sites, vessels, and offshore platforms.
5G and Oil and Gas Industry
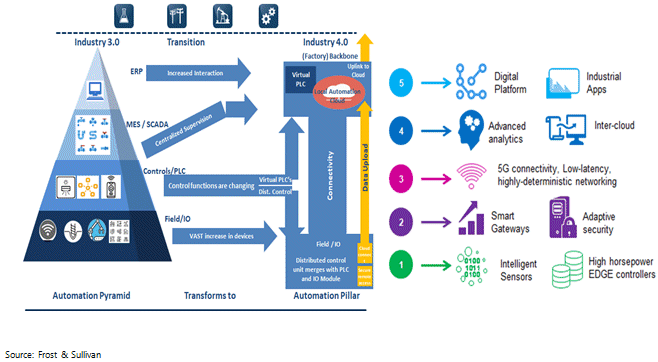
The oil and gas industry is known to be a heavy user of reliable, secure, and resilient networks for providing seamless communications for their daily operations. The new mission critical applications in the industry are developed on robust computing platforms. These are also bandwidth intensive, and are delivering richer information to the control center. Network operators have continuously evolved to deliver cost-effective technologies to fulfill legacy, as well as new application requirements without compromising on network performance and reliability. Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), with its service oriented virtual private network (VPN) capability, has been fulfilling such requirements by converging applications. Both MPLS and VPNs were deployed in climate-controlled operations centers in environmentally challenging locations. LAN based Ethernet, WiFi, and LTE technologies are now being leveraged for industrial applications, and thereby providing a starting point for increasingly demanding, transformative automation using 5G networks. With 5G networks, enterprises’ private and exclusive networks can now be better configured to their exact performance requirements. Additionally, cellular-virtual campus network solutions and network slicing features of 5G standalone further strengthen the network performance requirements, as well as data privacy, real time control, massive connectivity and high bandwidth needs. This is possible because of the non-dependency of such networks on the public networks, higher control on the deployment environment, flexibility of designing the networks for optimized and real time performance, higher reliability and availability of networks, and most importantly, the ability to deploy more stringent security and data privacy policies.
5G technology has gone live at a time when oil and gas industry itself is going through significant transformation and greater automation leveraging technologies like IoT, machine learning, and robotics. From a process automation perspective, many industrial processes are already automated, and oil and gas enterprises continue to go after greater efficiency, and production speed by leveraging existing and new age communication networks like 5G. 5G doesn’t necessarily define the industrial processes, but rather acts as an enabler of new use cases and operating models. To start with, 5G networks offer immense opportunity to replicate the function of wired systems for various controllers, switches, sensors and actuators. Additionally, with the wider adoption of 5G networks, there will be several opportunities to integrate 5G as an integral part of the evolution of industrial automation as production lines, machines, and process are improved and redesigned. An immediate opportunity is to leverage 5G networks to replace the existing wired LANs. One can argue that LTE and WiFi could also do this, but these generally don’t support the layer 1-2 performance needed for the high bandwidth intensive applications. 5G can therefore as proven by testbeds and PoC’s can easily meet these critical requirements. Additionally, there is an increased interest of oil and gas companies in IIoT; which comes with its own set of unique and complex needs, i.e. extreme mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low latency, massive IoT systems (<10 ms latency, 99.9% availability etc.). The high diversity of devices in oil and gas enterprises, i.e. sensors, automated guided vehicles, untethered AR / VR, security cameras, robotic controls etc. generates very different kind of requirements for throughput, mobility, latency, density, availability, and power. LTE and WiFi could meet some of these needs, but the ones falling under the category of URLLC (ultra-reliable low latency communication) could only be addressed through 5G networks.
There is no denying that there are several 5G use cases in the oil and gas industry, and we are still scratching the surface when it comes to the identification of potential use cases. With that being said, oil and gas companies in the region could leverage what is being done by their peers in the global markets, and replicate those use cases wherever possible. Some of the most relevant 5G use cases among the regional oil and gas enterprises are analyzed below.
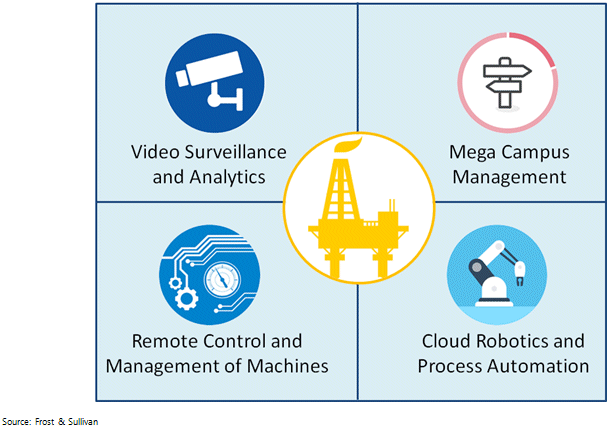

Physical security at oil and gas enterprises is as important the production itself. Wireless video surveillance is an effective and proven way to manage the security of campuses of oil and gas enterprises and drilling platforms. Based on various market estimates, the global video surveillance market will surpass $60 billion in 2025. Mounting cameras on drones, land vehicles, and in places that are difficult to reach through fixed cables is being made possible by wireless broadband. The cameras can deliver footages to enhance critical awareness and decision making for a variety of situations. As an example, drone-mounted cameras can help address seismic changes, fires, and natural disasters more effectively; terminal operators could proactively inspect container ships before even they reach the port; allow operators of wind farms to proactively detect problems with turbines. Video analytics could significantly enhance the quality, security and efficiency by enabling intrusion detection, automatic fault detection, and control of robots. Similarly, search and rescue operations could leverage the camera drones and video analytics to survey remote areas without human intervention.
Wireless video surveillance requires high bandwidth capacity, and oil and gas enterprises need robust uplink capacity and throughput provided by 5G to deploy high-resolution and high density cameras. Enterprises would also need 5G networks to combine 4K cameras with video analytics, and support precise object detection on assembly lines.

VR, AR and MR are not only changing the consumers’ experiences, but have become very relevant in the enterprise space as well. Both AR and MR are supporting collaboration for diagnostics and maintenance, which is a high value use case for the industry. Oil and gas enterprises in too can use AR and MR technologies to enhance employee training, and develop better and faster ways to enhance employee productivity. As an example, VR technology is now being used to recreate real life scenarios for workers to safely practice their skills. It could even support remote co-working, thereby creating efficiencies by allowing collaboration among employees in virtual spaces. Additionally, it could also create efficiencies by providing data access to employees as and when required; and also allowing them to interact with data, applications and the environment around them in new ways. Given the increased adoption of the digital twins, i.e. the virtual counterparts of the physical assets or physical sites, would also be a potential opportunity in the industry.
5G will help attract enterprises by delivering the required throughput and capacity for the transmission of high-resolution and framerate videos. Cloud deployments will deliver the ultra-low latency required to compensate for content and processing times. Additionally, 5G network slicing will enable the use of a defined quality of experience (QoE) to ensure consistency. 5G will ensure consistent transmission for AR applications at ultra-low latency and high reliability. While, edge computing will address the network delay and ensure the security of sensitive data.

Similar to other industries, oil and gas enterprise too would like to use machines like drones, cranes and robot arms in remotely controlled way. One of the main purposes of remote machines and video surveillance is to move in the direction of unattended production environment to control costs. The idea is not only to boost the efficiency in areas that are difficult to reach, but also increase the safety level of workers by keeping them away of hazardous environments. The industry is slowly moving towards fully automated remote sites performing various production tasks, and not just the mere management. These are the key drivers for private wireless networks deployments. Machines needing remote controls are mobile and require reliable and ultra-high speed wireless connectivity and that too between long distances. The current control requirements could be met with LTE, while future requirements through 5G.
Private LTE network can certainly support machine remote control applications, but the higher uplink capacity needed for data transmission to the command center is only possible through 5G. As an example, private LTE network could support high definition video streams, but 4K videos are only possible through 5G. More importantly, data-intensive control methods such as haptic feedback and increasing density of remote-controlled machines will demand for 5G networks.

In a bid to simplify their processes, increase efficiency and eliminate human errors, automation and robotization are gaining significant adoption across industries, including oil and gas. The opportunity for cloud robotics and process automation is immense, but it demands robust networks that can deliver reliability, low latency with high bandwidth and an ecosystem of machines supporting LTE and 5G in their subsystems. Wireless connectivity eliminates the constraints of yesterday’s static factory production lines, allowing machines to become mobile, and thereby reduce time taken in reconfiguring the production environment and change requirement needs.
Private LTE networks could support cloud robotics and process automation applications to an extent. However, 5G networks (by enabling higher capacity and low latency) are needed for performance improvement and to create more opportunities for deeper automation. Moreover, network slicing will enable oil and gas enterprise to support robotics use cases in production and non-production environments. With the addition of URLLC, 5G will enable simpler machine control to be processed in the cloud. This will further eliminate the need for local programmable logic controllers, and create more opportunities for cost reduction and machine coordination.
Conclusion and Outlook
Oil and gas enterprises in the region have continued to transform themselves amid immense challenges. Beyond the smooth execution of operational applications for current operations and production, there is a clear opportunity for them to transform their communication and application technology to reap the full benefits of 5G networks. Oil and gas enterprises must expand their network to new oil fields. With that being said, it is pivotal for oil and gas enterprises to innovate at a faster pace and implement this innovation in the new and existing oil fields.
The Middle East is one of the leaders in 5G roll outs across the globe. As operators continue their rollouts and move beyond consumers, B2B applications are expected to pick up. Most regional O&G giants are already in process of evaluating and conducting PoC’s on the ways 5G can benefit them in terms of automation and efficiency, but more can be expected as new business models emerge that would support these enterprises in revamping certain business processes or finding new ways to tackle their challenges with faster communication and better coverage. The regional oil and gas enterprises have a tremendous opportunity to leverage the 5G infrastructure to solve a variety of existing and unforeseen challenges. There are enough use cases to test the waters and then further build upon them.



