Introduction
The rise of industry 4.0 is upon us. Organizations are mapping out their digital transformation plans as industries move towards automation and efficient business operators. With the introduction of 5G, this transformation is expected to accelerate as traditional industries are getting better equipped to operate and grow with the benefits 5G promises to offer.
Embarking on a company-wide digital transformation is not a simple undertaking. It comes with its challenges. Needless to mention that digital transformation would require a wide range of ultra-high speed communication networks connecting hundreds and thousands of devices to the 5G network. eMBB, mMTC and uRLLC are expected to drive several IoT and digital transformation use cases across industries, e.g. smart home, smart metering, process monitoring and optimization. One of the most notable innovations of 5G is network slicing, which enables networks to be segmented to meet the requirements of specific services whilst ensuring guaranteed resilience at low latency. For example, one network slice could be configured to support low latency applications such as augmented or virtual reality, while another is created to ensure the highest levels of availability, for applications in healthcare or for autonomous cars. By moving away from the one-size-fits all approach of current networks, slicing provides greater flexibility to meet specific service needs of use cases.
In order to leverage the full capabilities of 5G and translate them into significant improvements, the infrastructure of the organizations too will have to be upgraded to a certain extent, which fundamentally restructures the machine-to-machine connections, as well as the way traditional connections are made. Today, industries are facing significant challenges to drive the required digital transformation; some of the key challenges are mainly driven by:
- Poor level of digitalization of industry production environment: Most factories are isolated introducing fragments network devices and platforms which is posing a significant challenge to have a unified data collection, and monitor the status in a holistic way.
- The major dependency on wired networks: Currently 95% networks in the industry campuses are wired, with complex cabling and difficult operations, wireless connections account for 5%. Most of wireless connections are based on the Ethernet, which lacks reliability and stability.
- Poor Network performance: The existing wired connection of industrial Wi-Fi wireless network connection in the industry campus has bottlenecks in terms of flexibility, scalability, bandwidth latency and reliability.
- Poor Coverage: One of the other major challenges at existing and new facilities is the ability to seamlessly expand the network coverage whilst ensuring high reliability and speeds of the bandwidth.
We can safely say that 5G is the future, and the challenge now is to identify the use cases that can leverage the 5G technology to its potential – Virtual Campus Networks (VCN) is one such use case. There are several industries that operate mega and multi-site operations, and as a result, they are plagued by massive challenges in operating, monitoring, maintaining, and securing such diversified and complex sites. The challenges are not limited to the operations alone, but also to the efficiency and speed of execution. The whole premise of VCN is built on solving this issue, which is discussed further.
Why 5G VCN?
Oil rigs, gas exploration sites, universities, stadiums, mining sites, and other sites with diversified and remote infrastructure and large pool of workforce are known to encounter challenges around capacity, density, coverage, security, high operational cost, and complex management. By leveraging 5G networks, VCN offers a solution that brings in maximum device sharing and total isolation of frequency spectrum, and function synchronization between the dedicated network and public network to address the challenges mentioned earlier.
5G VCN provides a virtualized network (from public network) which is independent and dedicated to provide private network services for the campus. For organizations, they get access to dedicated network capabilities and lightweight assets to deploy digital infrastructure; while operators realize spectrum and network potential, and incremental benefits by commercializing the network capabilities. Other key benefits of 5G VCN are identification and segregation of users between public and private networks, guarantee security and low latency gateway localization, and convenient service provisioning on operator’s dedicated networks.
VCN Solution Architecture
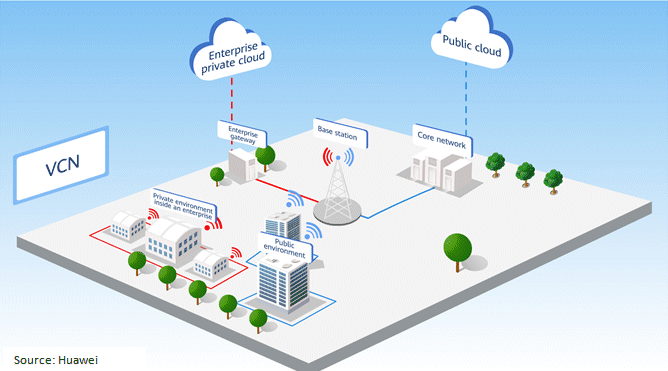
Generally, organizations require their campus data to be used and forwarded only within their organization. The 5G VCN can be easily deployed to meet this requirements whilst high-density, multiple-user access, reliability, security. The following figure presents the basic 5G VCN solution architecture.
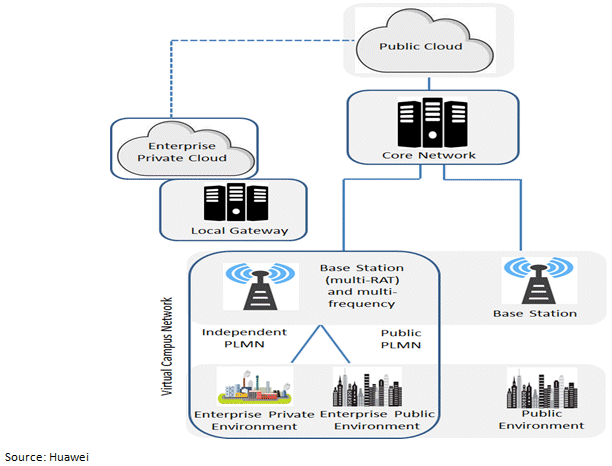
5G VCN Application and Opportunity for Industries
5G is aggressively embedding across the consumer and business segments. Regional telcos have been leading the 5G adoption by rolling out the 5G sites. STC rolled out 450 sites in Feb 2019, Etisalat completed 700 5G sites, and ZAIN too has announced that it has deployed 2000 sites in Saudi Arabia in October 2019. Telcos will have a great role in transforming the businesses across industries, and through VCN they can further expand their role, especially among the campus-based verticals. With the advent of digital technologies, like IoT, AI, RPA, and VR/AR, the campus-based verticals would have a great challenges to cope up with the increasing demand for massive concurrent connections, ultra-low latency, and security. As the current network architectures would never be sufficient to support these critical requirements; 5G VCN will come into play to solve these challenges. It would add up vivacity to various fields, serving industries, as well consumers. Below are some of the opportunities across campus-based verticals for VCN.
Oil and Gas
Exploration of oil and gas is an ongoing activity for growth. At the same time, industrial safety and security has always been a worrying aspect in this industry. Oil and gas platforms’ remoteness and isolation, extreme operating environment, harsh sea conditions, strong and unpredictable winds, water, and high temperatures are some of the many challenges strengthening the need for a robust communications system. Routine operations alone require the transmission of an insuperable volume of data and reports on logistics, supply, production, etc.
Many of the communications from oil and gas platforms to site and vessels depend on satellite links, which are not only expensive, but also complex to implement and manage at such a remote location. Intelligent, automated, and unmanned exploration methods are inevitable, but they would need network architecture with robust connectivity (high speed and low latency) which is dedicated and secure. 5G VCN can create a secure, robust, reliable and low-latency private network in unmanned areas, and dynamically monitor the production process in real time. Maximizing the production efficiency and remote monitoring and real time decision making are the most obvious direct benefits.
Education / University Campus
University campuses have witnessed increasing demand to provide seamless and consistent wireless coverage across their campus for content sharing and collaboration. Today, the average student has 2-4 Wi-Fi enabled devices; even faculty members carry various mobile devices (e.g. phones, tablets, etc.). The learning initiatives in the education industry continue to move towards online testing platforms and multimedia delivered over wireless. This brings multiple challenges to the traditional network to cater to this exponential demand:
- Outdoor solution to cover large areas in the campus, like studying halls, labs, and dorms
- Support high density areas
- Central management system, visibility, control and flexibility
- Security
5G VCN can seamlessly address these challenges by deploying the base station inside the campus as well as the Multi-access edge computing (MEC) in the campus data center which could be near to the base station. This deployment is characterized by data security and low latency, which will enable users across the campus to have seamless and consistent internet experience.
Expos / entertainment activities
Mega events attract large pool of visitors, where an outstanding networking infrastructure is crucial to cater to the massive demand for connectivity. The dynamic VCN deployment could be used even for such short-term requirements. In this deployment, the VCN based station is temporarily deployed in a specific area and the MEC is deployed in a fixed location (e.g. data center) for a long time. This mode is used to ensure secure data transmission on dedicated networks in the case of heavy traffic volume.
Opportunities for Operators
Industry 4.0 introduces wide spectrum of technologies, which emerging use cases are significantly dependent on. 5G is one of such technologies which would deliver low latency and ultra-high bandwidth, thereby enabling real-time decision making through analytics. Many of these use cases may not be addressed by existing public cloud platforms; which in a way is a great and immediate opportunity for telecom operators to deploy the MEC closer to the enterprises and capitalize on their existing infrastructure; while on the other hand, enterprises and third-parties will be able to innovate new applications and business models such as (AR/VR, IoT, analytics and other real-time and latency sensitive applications) by using 5G.
Cloud Computing is expected to go through a phase of decentralization. Edge Computing is coming up with an ideology of bringing compute, storage and networking closer to the users; thus in the near future, multiple smaller clouds will be common, and would also enable users to get all cloud capabilities (faster data processing, analytics, AI, AR/VR etc.) closer to them, that will enhance their experience. A strategic imperative to telecom operators is to benefit from this shift as enterprises are moving the edge applications into the edge cloud; telecom operators will have to be the facilitator and orchestrators to help enterprises in deploying, managing and operating their edge clouds.
Undoubtedly the use case built on emerging technologies will dominate, and 5G along with its preferred companion, i.e. IoT would be a critical enabler. IoT ecosystem is complex by nature, which includes an IoT platform, connectivity, as well as an exponentially increasing number of devices. Having said that, telecom operators will have an opportunity to package and offer a complete end-to-end solution to enterprises. Additionally, the services around the IoT such as IoT platform on MEC, 5G connectivity, devices management, and monitoring, and adjacent solution management like analytics and AI would be incremental opportunities. It is worth mentioning that the IoT scenario is also applicable for other emerging applications of gaming, AR/VR, and RPA. Given that 5G would be the underlying and critical enabler here, and the regional telecom operators have commercially launched 5G, there is significant headroom for growth as well as 5G infrastructure monetization opportunity for telecom operators.
Conclusion and Outlook
With several campuses aiming to enable digital use-cases via 5G, the question is not “why” or “when”, but instead “how”. However, the challenges in connecting remote sites and campuses are still a hindrance in driving this transformation. There are several use cases for VCN that leverage the robustness and reliability of 5G networks. On one hand, industries are embarking on their digital transformation and industry 4.0 journeys, and on the other hand, telecom operators are vigorously hunting for use cases to monetize their investments on 5G. There is clear evidence that VCN is the need of the hour for multiple industries, and its deployment models are proven. The vendor ecosystem appears to be ready to drive VCN use cases. Huawei in particular showcased its capabilities, as well as its actual VCN use case at the recently concluded 2019 Gitex. It is now up to the telecom operators to lead from the front and capture this opportunity before their competitors do.



