One of the biggest stories that emerged during the pandemic was the surging demand for last-mile food and grocery delivery. Companies like Meituan, Uber Eats, Just Eat Takeaway, and Walmart Grocery came to be on speed dial. As the last-mile food and grocery delivery market continues to boom, our research forecasts revenues to almost triple over 2020-2025 to top $72 billion. What are the key growth opportunity areas? What themes will define the market in the short- and medium-term? How should companies strategically respond? Which companies are pushing the envelope in terms of innovative services and solutions?
Today, almost 60 competitors with revenues over $1 million are battling it out in the highly lucrative last-mile food and grocery delivery markets in the US, China, and Europe. As the competition intensifies and consolidation ensues, we have identified six major trends that will shape market dynamics over the next 4-5 years:
- Quick Commerce – the next big idea
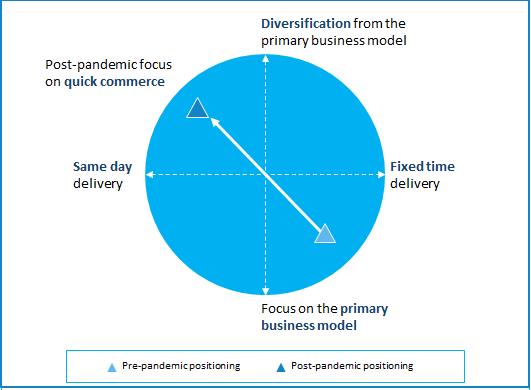
The COVID-19 pandemic has prioritized consumer safety and convenience, creating ripple effects accelerating the demand for same-day deliveries. Last-mile food and grocery delivery companies are pushing towards less than 30 minutes deliveries and are incubating a new category called “quick commerce”. Operators are innovating further to reduce delivery time to less than 10 minutes.
One of the forerunners in the quick commerce space has been Delivery Hero. Since launching quick commerce operations in Europe in 2019, it has collaborated with over 80,000 local businesses, operates over 600 dark marts across 35 countries, and recorded an astounding 400% Y-o-Y growth in Q1 2021.
Exhibit 1: Focus on Service Diversification Post Pandemic
Source: Frost & Sullivan
- Shared mobility operators to straddle goods and people transport
Last-mile delivery, for food or groceries, in partnership with restaurants, e-Commerce companies, or hyperlocal grocery stores — presents a massive opportunity for shared mobility operators. At the most fundamental level, both last-mile delivery and shared mobility are underpinned by a similar technology with shared mobility vehicles capable of being used flexibly for both goods and passenger transport. In fact, during the pandemic, several shared mobility operators repurposed their fleets to tap into the flourishing last-mile delivery sector. A notable example was ride-hailing giant Didi, which moved to offset the steep fall in its active user base by diversifying into home deliveries.
A raft of new developments like autonomous vehicles for passenger and goods transport, vehicles with larger trunks to accommodate goods delivery, e-Cargo bikes, etc., will define the future. We also believe that the engagement of shared mobility operators with last-mile delivery will deepen. This is already evident from the examples of Lyft, Bolt, and Uber in the US, Didi in China, and BlaBlaCar, Green Mobility, and Bird in Europe. All of them have ventured into the last-mile delivery space.
- Mergers & acquisitions to be sparked by service diversification, operational efficiencies, and profitability imperatives
Last-mile delivery and grocery operators are moving towards the next big revolution – quick commerce impelling mergers & acquisitions (M&As), a strategy seen as critical to boosting operational efficiencies and profitability. More significant participants, including retail chains, e-Commerce companies, shared mobility operators, and autonomous mobility firms are set to aggressively pursue M&As. As players step up their quest for service diversification, we have seen a spate of mergers like UberEats with Postmates, Just Eat Takeaway with GrubHub, and DeliveryHero with InstaShop and Honest Foods. Notably, after acquiring Takeaway and GrubHub, Just Eat instantly became the food delivery leader in Europe, expanded its presence to 24 countries, gained a 24% share in the US market where it had earlier lacked a presence, and became the largest food delivery company outside China.
Simultaneously, partnerships and collaborations with non-industry players have been aimed at developing non-core competencies, much like Meituan has done with its partnership with Nvidia, Valeo, and Icona for autonomous delivery.
- Fleet electrification to be underpinned by sustainability and micro-mobility
One of the most prominent trends we have been tracking pertains to fleet electrification for last-mile deliveries. This has been in response to the sustainability agendas of cities, many of which now champion ultra-low emission zones or zero-emissions vehicles. Electric mobility ranges from mellow vans (somewhere between bicycles and vans that can carry higher loads) to micro-mobility modes like e-Cargo bikes and e-Scooters, and urban tricycles that carry groceries.
Gorillas, a European-based quick commerce company, has differentiated itself with its focus on sustainability by employing a fleet of bike couriers.
- Tech innovation to be a vital growth catalyst
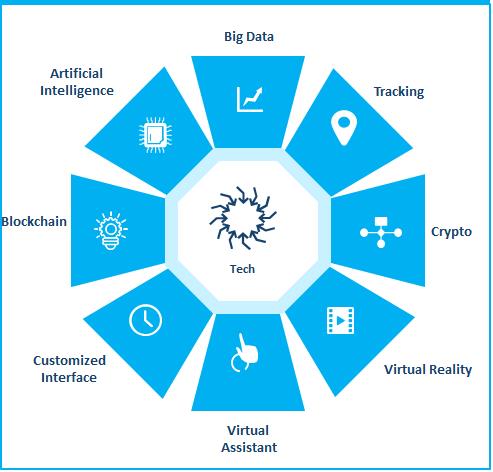
Blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), virtual assistants, Big Data, smart tracking, advanced analytical insights, customized interface, virtual reality, and crypto will drive market transformation. AI-enabled, dynamic route optimization will improve delivery times, enable cost reductions, and enhance customer satisfaction. Blockchain and 5G will promote more efficient and cost-effective last-mile deliveries.
Meituan has been a market leader in using contactless delivery, dynamic route optimization, smart tracking, and advanced analytical insights.
Technology innovation is also becoming a significant competitive differentiator. Delivery Hero, Amazon, and Meituan are trying to leverage technology in a bid to own the whole value chain. For instance, Meituan is becoming a super app, offering 200 different services ranging from food to travel.
Exhibit 2: Key Technology Trends Fueling Growth in the Last-mile Delivery
Source: Frost & Sullivan
- Autonomous tech to support contactless deliveries, boost the adoption of drones, bots, and autonomous vehicles
Health and hygiene concerns, coupled with rising labor costs, have strengthened the appeal of contactless deliveries. This, in turn, is shining the spotlight on autonomous delivery technologies.
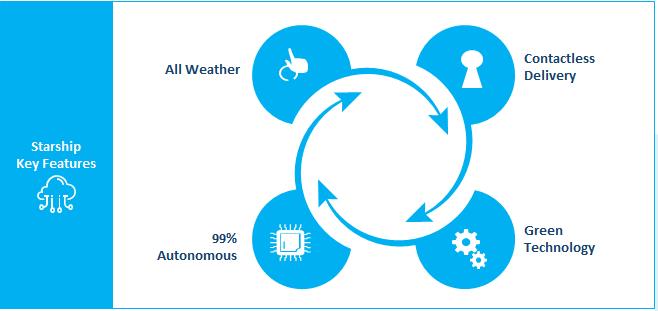
It is estimated that bot deliveries cost 60% less than manual deliveries. Such cost efficiencies, reinforced by greater regulatory clarity, will encourage autonomous deployments in the last mile delivery space. Starship, with its 1,000 autonomous bots, is one of the world’s fastest-growing companies. The company’s stand-out features include contactless delivery, green tech, 99% autonomous deliveries, and partnerships with companies like Dominos, Just Eat Takeaway, and DoorDash.
Exhibit 3: Contactless Autonomous Delivery Surged During COVID-19, Starship a Key Player
Source: Frost & Sullivan
As the market evolves, companies need to look at a range of strategies to optimize the exciting growth potential that it presents. Exploring complementary partnerships, new business and delivery models, embracing innovative technologies that support sustainable operations, resource optimization, and cost efficiencies will spur long-term growth.
Schedule your Growth Pipeline Dialog™ with the Frost & Sullivan team to form a strategy and act upon growth opportunities: http://frost.ly/60o.



