By Riti Newa, Research Associate, Industrial Group
Industrial cybersecurity has been garnering widespread significance due to increasing number of cyber-attacks specifically targeted at the manufacturing and utility process environment (for example, the Stuxnet attack, the Ukrainian power grid attack, the Dragonfly malware attack etc.). Cost of cyber-attacks pertaining to cyber physical damages that occur as result of cyber breaches are high among these industries. Cyber-attacks in energy and utilities industries alone cost an average of $13.2million/year.
Increased susceptibility of industrial control systems (ICS) to external and internal threats in recent years is hence driving higher investments for industrial cybersecurity. However, implementation of cybersecurity solutions is still not common among end users due to the high complexity of security architecture and the unclear returns on investment (ROI).
Robust cybersecurity practices, deployment of security tools for multi-vendor ICS landscape and need of lifecycle management of the deployed security architecture is implying high overhead cost for end users. Service providers are focusing on lowering the overall cost of ownership and reducing complexity through industrial cybersecurity as a service approaches.
Cybersecurity as a Service Approach
In an ever changing threat landscape, end users want scalability and flexibility in their cybersecurity approach. Service providers have started to transition to cybersecurity as a service models to integrate pricing flexibility in their services and address needs of the market. A service based approach to cybersecurity has given rise to service models such as software as a service (SaaS), assessment as a service, platform as a service (PaaS) etc.
Market Drivers
Industrial cybersecurity services will be seeing significant growth with wider market acceptance of service models among end users. The major market drivers for industrial cybersecurity as a service will be the need of lifecycle services due to growing skill shortage and reducing the overall cost and complexity.
Lack of in- house competency
The demand for cybersecurity services is escalating but there is skill deficiency for the required sophisticated cyber risk services. Industries lack dedicated security teams to manage the deployed security architecture and hence are investing on outsourcing cybersecurity services. Lack of in- house competency is accelerating the need for cybersecurity as a service that could provide lifetime management of the security architecture. Expertise as a service models that can allocate cybersecurity experts for threat monitoring, vulnerability assessment and automating the cybersecurity network management services have been growing popular among end users.
Increased cost and complexity
A holistic approach to industrial cybersecurity is growing increasingly challenging in the multi- vendor environment of the industry. End users want scalability in the security offerings to integrate the best practices of cybersecurity. Due to unclear ROI and increasing complexity in implementing cybersecurity in multi-vendor ICS systems, market players are providing a number of subscription based cybersecurity service models. Figure 1 below indicates the reduction in total capital expenditure (CapEx) and operational expenditure (OpEx) for industrial cybersecurity services provided on subscription basis as compared to maintaining in-house competency for cybersecurity.
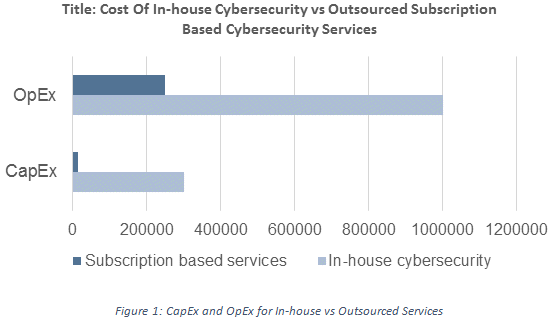
Subscription and contract based cybersecurity services allow end users to minimize capital funding costs and assess the state-of-the-art technologies without incurring an added cost for implementing and supporting hardware. Cybersecurity service providers are focusing on pay-as-you-go expertise by providing SaaS models on subscription basis to continually monitor and assess the industrial environment through security operation centers (SOCs) and assess the inherent risks in the environment.
Market Environment
Service providers in the industrial cybersecurity market have been focusing on presenting service based models that allow a high degree of scalability and enable integration of cybersecurity best practices. Automation vendors are providing a range of managed and professional services on subscription and contract basis to enhance the cybersecurity posture of their end users. Information Technology (IT) companies and start- ups are also providing managed security services on subscription basis to allow the services utilized to change over time. End users prefer the cybersecurity services on subscription basis that allow them to be periodically realigned with their dynamic security needs in the evolving threat environment.
With the increasing cyber awareness among end users and growing sophistication of the cybersecurity technologies, industrial cybersecurity services market will have a strong sustained growth in the coming years. To understand the trends, market growth environment, emerging service models and competitive landscape, please refer to the Frost and Sullivan study, Industrial Cybersecurity Services Market—A New Business Frontier for Profitability (K2C6-01).



