In 2019, Ransomware viruses hit two cities in Florida that made large ransom payments to gain back access to city files that were encrypted in the attacks. These breaches incurred insured losses of over $600,000 in Riviera Beach City and $500,000 in Lake City, leading to huge disruptions to normal life. The main challenge in front of Critical National Infrastructure (CNI) operators is the reliance of CNI on legacy IT systems and operational technology (OT) systems. These legacy systems, which were not designed with cybersecurity in mind, are now increasingly networked and connected to the internet to enable more efficient control and real-time monitoring. This has the effect of creating new vulnerabilities and potentially exposing the systems to cyber-attacks.
According to Frost & Sullivan’s research, Global Use-Cases for Cybersecurity Solutions in Critical National Infrastructure, the CNI cybersecurity market is projected to grow to $119.23 billion by 2024. This growth is thanks to the growing and evolving threat to CNI, and the creation of an increasingly competitive environment for cyber suppliers as cyber-specific firms have been joined by new market entrants from the defense and commercial IT sectors.
To schedule an exclusive interview with Shaurya Singh on this topic or to know more about our cybersecurity practice, please email Mariana Fernandez, Corporate Communications: [email protected].
The Frost & Sullivan security team has been tracking cybersecurity incidents on CNI around the world over the past years. By following these incidents, the team has gathered insights on recent cybersecurity trends, historical attacks, and what are the growth opportunities for the security industry.
Major Growth Opportunities in 2020:
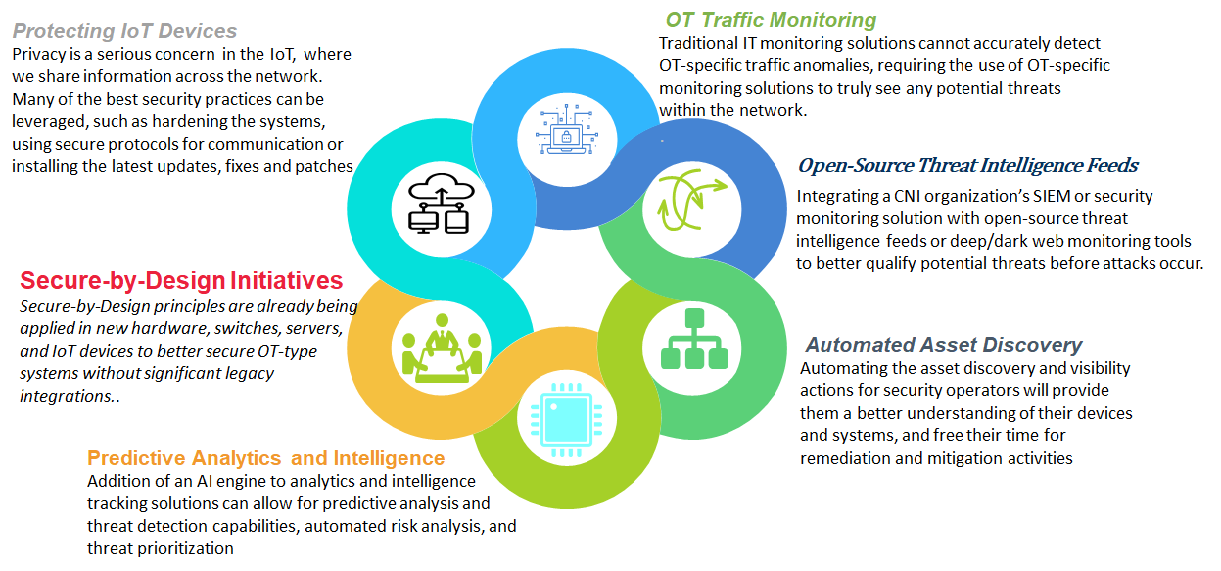
Trends that will shape the 2020 Cybersecurity in CNI landscape:
- Data breaches are likely to continue for as long as personal and organizational data remains a valuable black market commodity. Sensitive data of CNI’s in the wrong hands can prove disastrous leading to huge losses and disruptions to normal life.
- Many critical infrastructure technologies are based on legacy IT and OT systems which are poorly secured, posing serious risks to utilities, and ultimately national security. Plugging these loopholes and stopping the exploitation of these loopholes by cyber attackers will play an important role in the cybersecurity of CNI.
- In the future, as the reliance on virtual infrastructure in CNI becomes acceptable; the physical redundancies may be abandoned, which would make it easier for an attacker to carry out a devastating breach that can cause real damage. Maintaining physical backups or other physical redundancies can reduce the impact of a successful attack.
- In 2019, an increasing number of institutions overseeing the critical parts of daily life – suffered IT system shutdowns as a result of ransomware attacks. The repercussions of data breach and denial of service can inflict millions and even billions in losses or disturbing the essential services for maintaining daily life. The cyberattack on electrical supply utilities of Johannesburg, South Africa, in 2019 leading to loss of electrical supply to residents and business is an example of a ransomware attack. The trend of ransomware will continue in 2020.
- As CNI organizations increase their reliance on mobile devices and on IoT devices, hackers will put more effort into exploiting vulnerabilities. A growing problem is rogue mobile apps that look like trusted brands but are designed to steal sensitive information. In IoT, more and more devices are getting connected to the internet every day without any effective policies and governance leading to a lot of loopholes to be taken advantage of. Challenges with cybersecurity involve device security, data security, and protection of individual’s privacy.
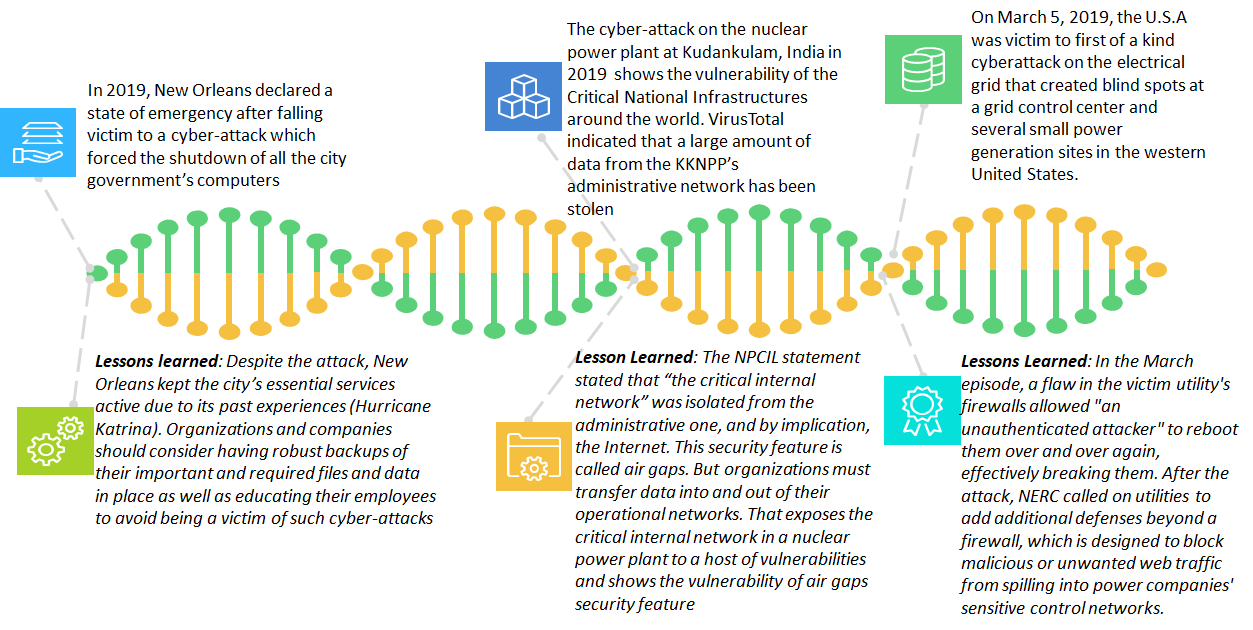
Recent attacks that are registered on the Frost & Sullivan Cyberattack incident tracker:
The importance of cybersecurity is on the rise. Our society is more technologically reliant than ever before and there is no sign of this trend buckling down. Safeguarding and having a robust cybersecurity plan for CNI can have a significant economic benefit by reducing the impact of a potential cyber-attack and increasing the effort for threat actors to attack the facility.



