Introduction
As we envision smart machines exceeding their capability being backed by intelligent sensors that ensure real-time data processing. These smart machines and devices are fully connected or well networked enabled by sensors. Deployment of fieldbuses enables real time for data transmission and two-way communication facilitating in time decisions that trigger course correction where ever required and all in real time.
Sensors are great enablers, rather unsung heroes in manufacturing transformation through digitalization. Digitalization deals with a lot of challenges. It addresses challenges in manufacturing while transforming the way factory operates. It also provides an end-to-end solution from programming supply chain through production to scheduling deliveries of finished products.
Sensor Vision Backed Transformation
Complete connectivity which enables sharing of real time data is the key to transforming existing factories/manufacturing units to smart. The end-to-end seamless integration starts from supply chain and logistics. Sensors become the key enablers of this transformation as they are the first to sense any object irrespective of operational environment.
Prior to transformation the issues of interoperability of sensor devices still need to be resolved through standardization. The step to transformation starts from the designers investing in design software. Companies should host the models on the cloud accessed through a shared portal. They should also use software supporting simultaneous versioning. Prototypes can be created from model with 3-D printing. Investment castings or circuit masks can be created from the same model.
For future fulfillments current design software claims to be collaboration capable, but real team software is needed (for example Digital Thread). All in the supply chain are concerned about the cyber security of shared systems and models-Risk Management.
Key Steps to Transformation
A multipronged approach is key to implementing steps toward achieving transformation not only of the manufacturing assembly but also the entire value chain.
The enablers of this transformation are:
- Adoption of IoT platform enables both remote monitoring and control. It facilitates real time decision making and implementation to ensure safety and process integrity.
- Depending on the process and data, to develop and use analytical software to enable auto course corrections
- 3D modulation and printing can be extensively used to perfect designs. Prototypes can be created from model with 3-D printing. Investment castings or circuit masks can be created from the same model
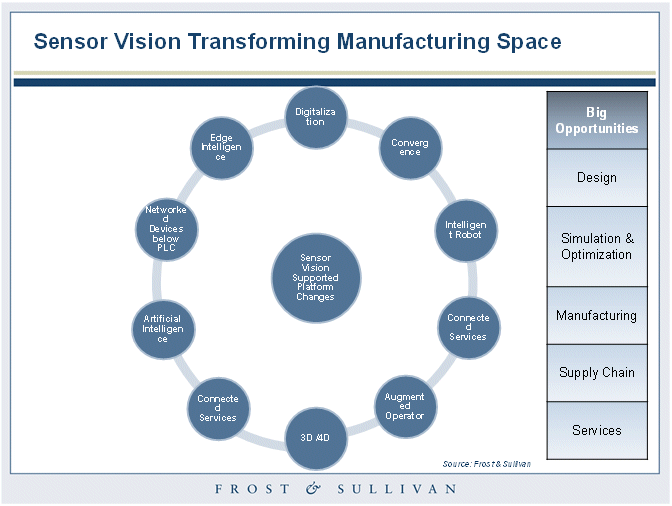
Use of intelligent sensors not only imparts intelligent decision making by machines/systems in real-time but it also results in higher productivity and yield, thereby lowering cost of production
- Implementation of edge analytics is highly beneficial in closed loop configurations
- Adopting artificial intelligence
Emerging Vision
Intelligent sensing technology has moved ahead in detecting and measuring any object virtually in most of the industrial automation applications. The digital transformation leading to intelligent factories of the future stands on four key planks:
- Transformation of human capital
- Federated manufacturing
- Cognitive platforms
- Valued new networks
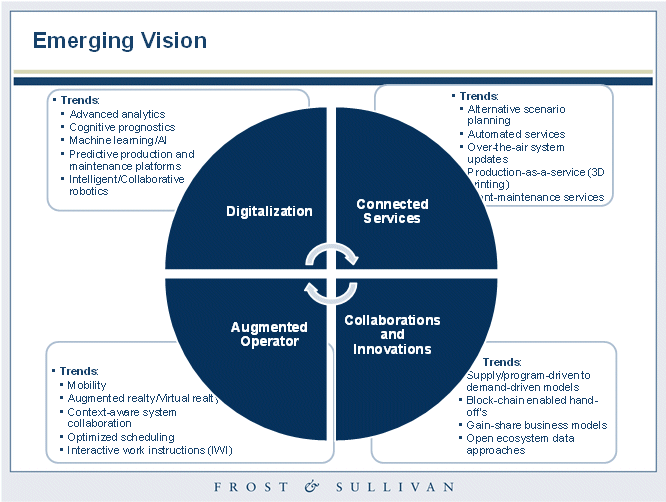
Transformation of human capital involves manufacturers to have large opportunities to drive plant efficiencies and boost innovation from design to manufacturing of new/ improved products. Transformation of human capital at the micro level/operational level includes activities from retooling to collaborative and autonomous machines. Some look at this transformation as dominance of machines. The cognitive platforms essentially are connected platforms which enable digitalization of the manufacturing systems. Smart innovations enable federated manufacturing. It is a much wider effort that involves various facets of manufacturing right from materials innovation through collaborative innovation to modular manufacturing. The valued new networks facilitate integrated supply chain where customers can pay for specifications.
Conclusion
Use of intelligent sensors with prognostic rather than diagnostic capability is changing the manufacturing space. Increasing customization in discrete manufacturing is likely to result in greater variations in the final product. The smarter communication on the factory floor enables automated change over on the assembly line. The question remains will the small batch manufacturing be a reality?. The integration of intelligent sensors and software enable digitalization is resulting in new business models, which are bound to support growth of business through centralized manufacturing and modular factories.



